
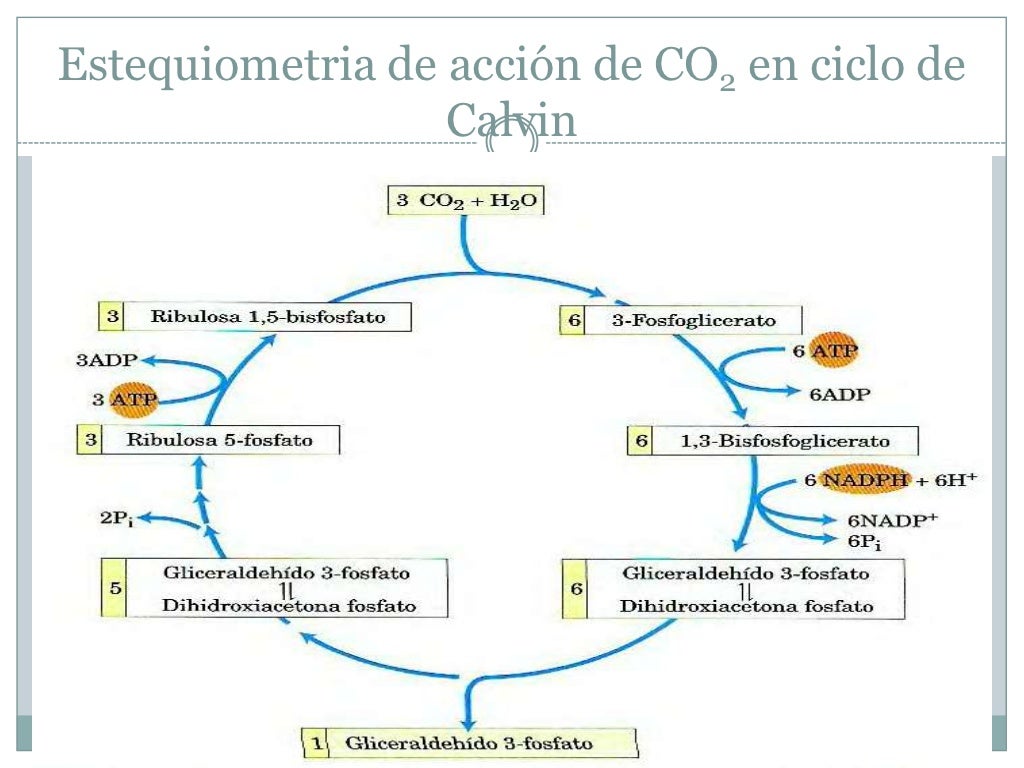
CalvinBenson cycle adapted from Taiz and Zeiger (Taiz and Zeiger
The Calvin cycle is the major CARBON-DIOXIDE fixation pathway, found in all in green plants and many autotrophic bacteria. In this cycle, one CARBON-DIOXIDE molecule at a time is added to the acceptor molecule D-RIBULOSE-15-P2 (RuBP) generating two molecules of G3P.

CalvinBensonBassham cycle in R. rubrum . Abbreviations 3PG
These reactions are also called the light-independent reactions because they are not directly driven by light. In the Calvin cycle, carbon atoms from CO 2 are fixed (incorporated into organic molecules) and used to build three-carbon sugars. This process is fueled by, and dependent on, ATP and NADPH from the light reactions.
The CalvinBensonBassham cycle (CBBc) reactions. The CBBc has three
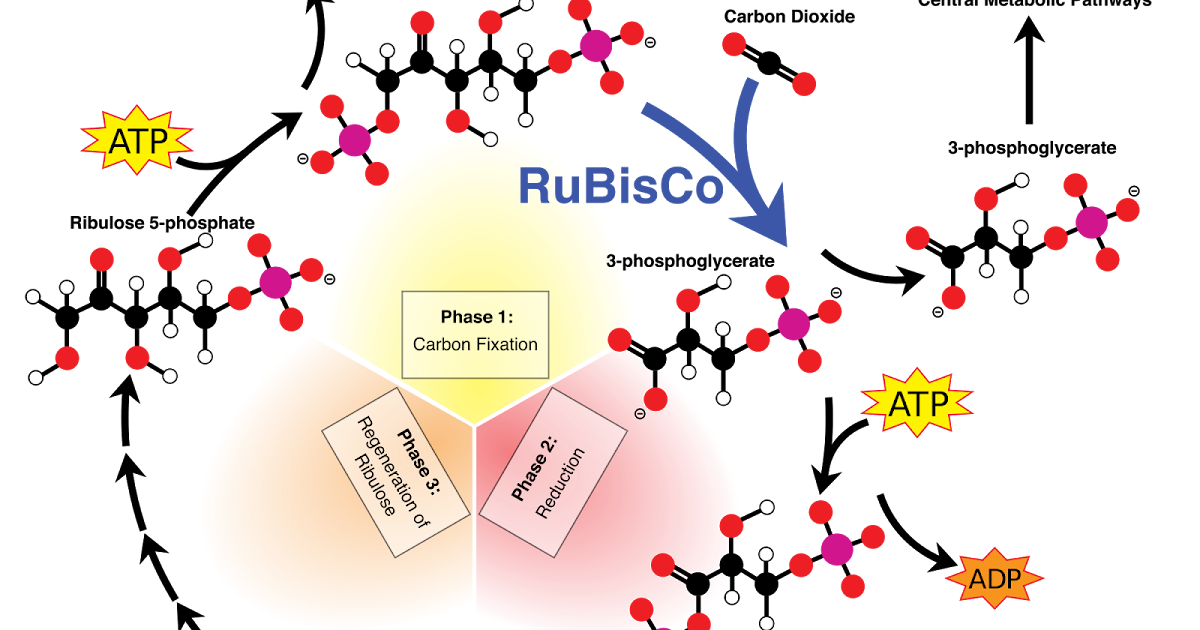
Figure 8.5. 2: The Calvin cycle has three stages. In stage 1, the enzyme RuBisCO incorporates carbon dioxide into an organic molecule. In stage 2, the organic molecule is reduced. In stage 3, RuBP, the molecule that starts the cycle, is regenerated so that the cycle can continue. In summary, it takes six turns of the Calvin cycle to fix six.
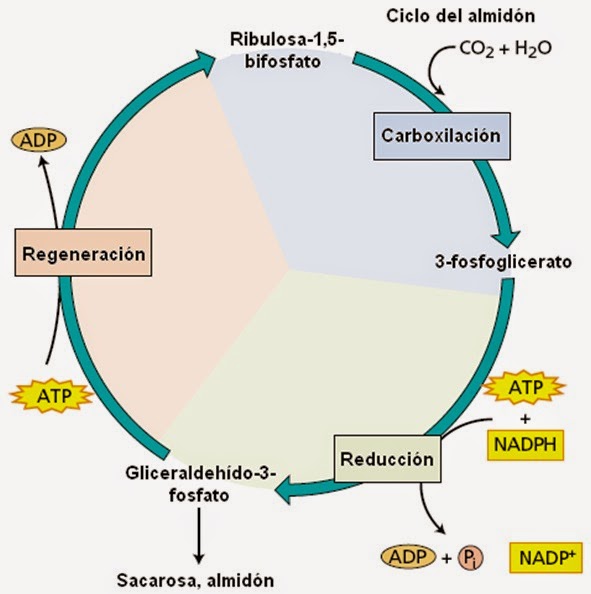
Reacciones oscuras.Ciclo de Calvin Apuntes de Bioquímica
El dióxido de carbono es capturado en un ciclo de reacciones conocido como ciclo de Calvin, o ciclo de Calvin-Benson en honor a sus descubridores. También se conoce como simplemente ciclo C 3. Las plantas que utilizan sólo el ciclo de Calvin para la fijación del carbono, se conocen como plantas C3.

CalvinBenson cycle (light independent reaction/dark reaction
The Calvin-Benson cycle assimilates almost all the carbon in plants and is thus among the most important biochemical cycles for life on Earth. It is believed to be self-sufficient in that it.
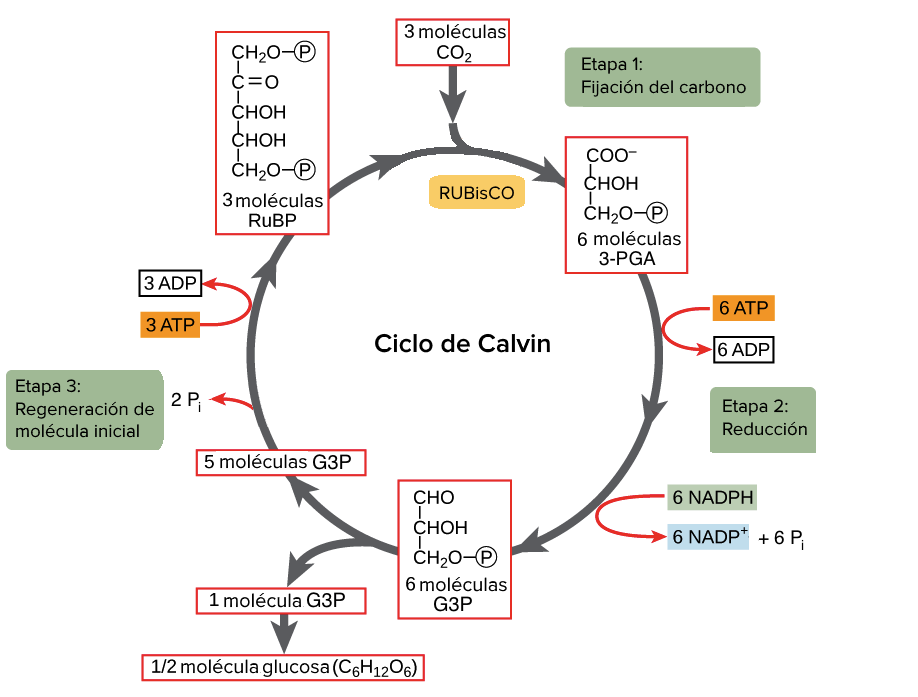
Guía para tu futuro El ciclo de calvin
The Calvin Cycle. In plants, carbon dioxide (CO 2) enters the leaves through stomata, where it diffuses over short distances through intercellular spaces until it reaches the mesophyll cells.Once in the mesophyll cells, CO 2 diffuses into the stroma of the chloroplast, the site of light-independent reactions of photosynthesis. These reactions actually have several names associated with them.

Ciclo de Calvin Benson YouTube
Patients and Controls. The SHEEP study design has been described in detail elsewhere. 8 In short, the SHEEP study base was composed of all Swedish citizens residing in Stockholm county who previously had not been given the diagnosis of myocardial infarction. Male cases were identified during 2 years (1992 and 1993), and female cases were identified during 3 years (1992 through 1994).
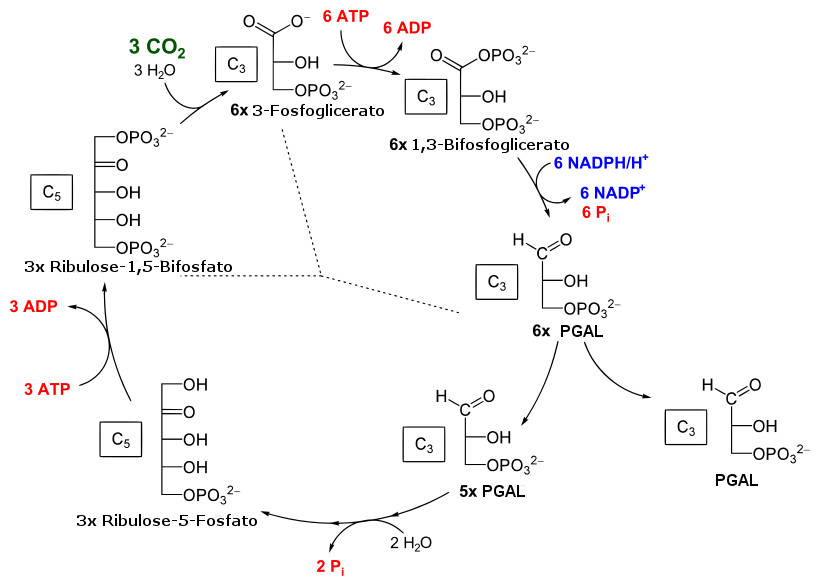
Ciclo de Calvin Biologia InfoEscola
The Calvin Benson cycle (CB cycle) catalyzes CO 2 fixation in all oxygenic phototrophic bacteria (cyanobacteria) and is present in at least 6% of non-cyanobacteria genomes [1]. The bacterial CB cycle has primary ecological importance in both aquatic and soil habitats. Cyanobacteria may constitute up to 25% of ocean primary production [2].
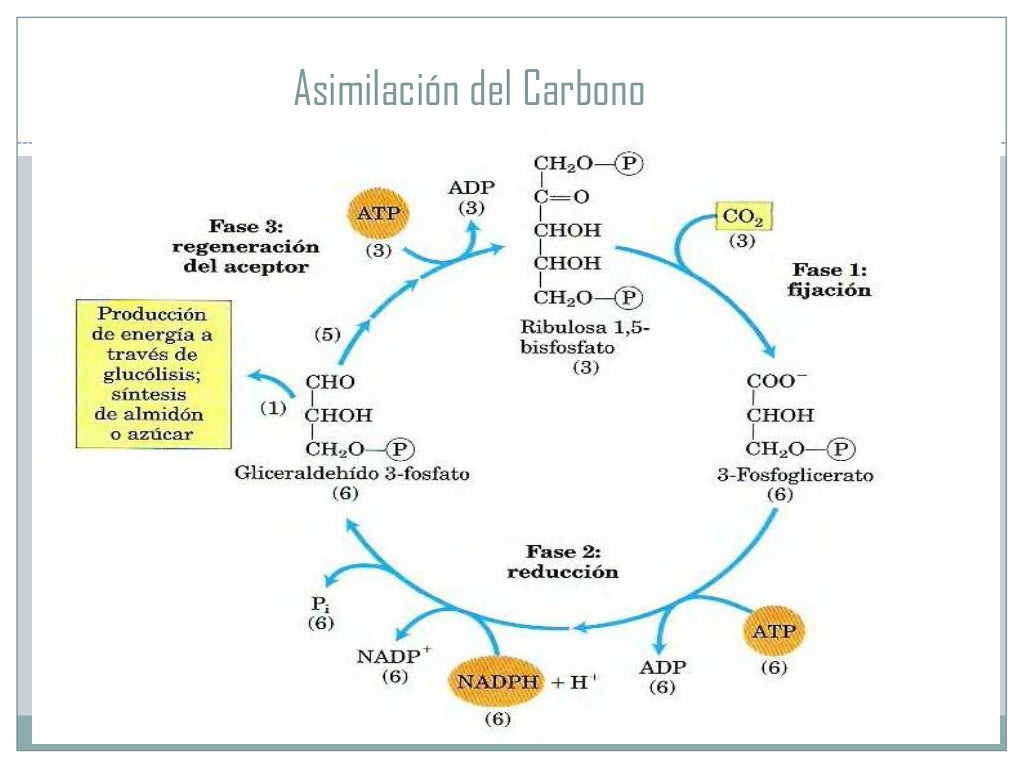
Ciclo de calvin
El ciclo de Calvin también es llamado ciclo de Calvin-Benson o ciclo de la fijación del carbono de la fotosíntesis. Se trata de una serie de procesos bioquímicos que ocurren en las plantas. Específicamente sucede en el espacio interior de los cloroplastos, llamados estromas, que a su vez están dentro de las hojas.
Fotosintesis Mind Map
Around 1945, the american chemists A.A. Benson, J.A. Bassham and M. Calvin [1] (Figure 1) tackled the task of identifying the first carbon-containing product of photosynthesis that had escaped all scientific investigation. After the World War II, these researchers had just acquired two new important technological allies in Berkeley, California:

Ciclo di Calvin BioPills
The Benson-Calvin cycle (or reductive pentose phosphate pathway) is the only mechanism in plants and algae, which can catalyze the net fixation of CO2, although some bacteria have an alternative mechanism. From: Encyclopedia of Biological Chemistry (Second Edition), 2013. Related terms: Oxygenase;
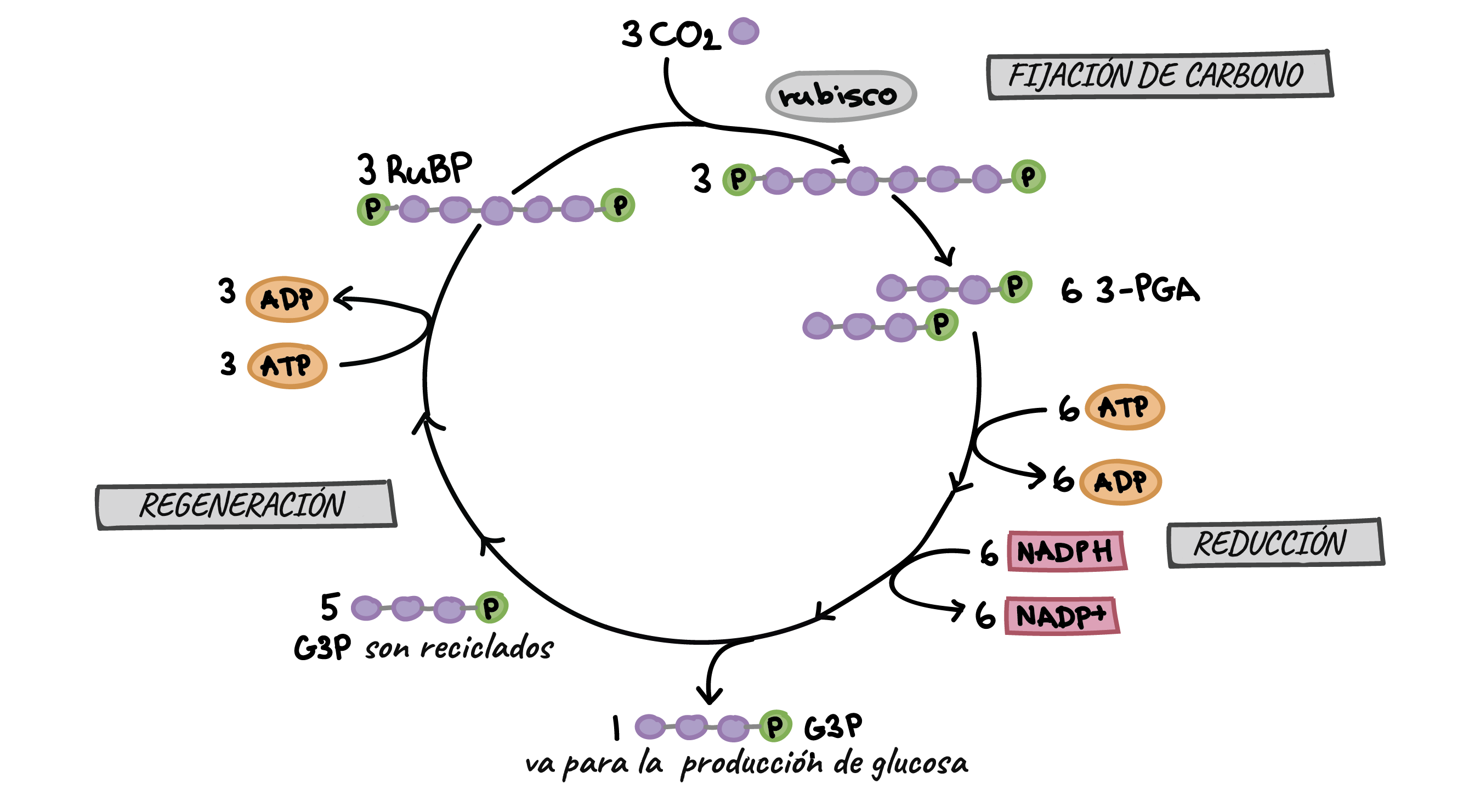
Ciencias de Joseleg Resumen del ciclo de CalvinBenson
As reações do ciclo de Calvin podem ser divididas em três etapas principais: fixação do carbono, redução e regeneração da molécula inicial. Aqui está um diagrama básico do ciclo: CO 2 Regeneração. [Veja um diagrama que mostra as estruturas moleculares] Fixação do carbono. Uma molécula de CO 2
As etapas do Ciclo de Calvin AgriScience O mundo das plantas
El ciclo de Calvin (también conocido como ciclo de Calvin-Benson o ciclo de la fijación del carbono de la fotosíntesis) consiste en una serie de procesos bioquímicos que se realizan en el estroma de los cloroplastos de los organismos fotosintéticos en la planta. Las reacciones del ciclo de Calvin pertenecen a la llamada fase independiente.
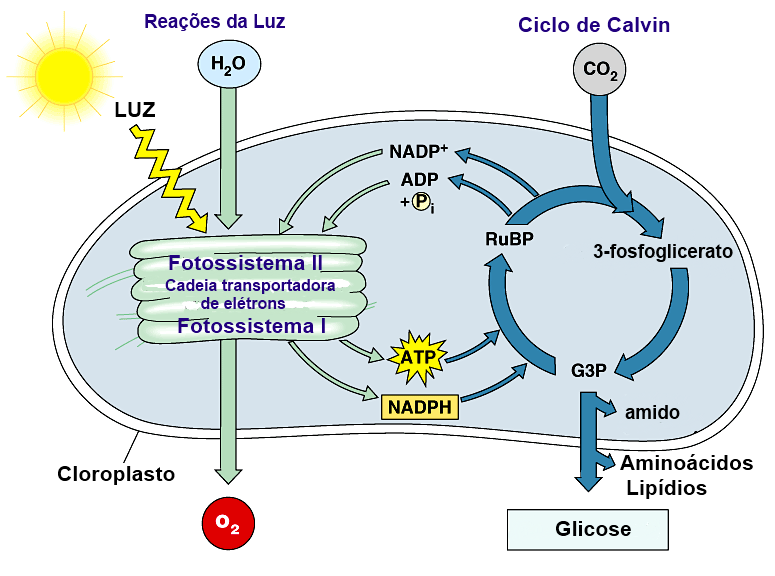
Ciclo de calvin
A fase química, também chamada de ciclo das pentoses ou de Calvin ou de Calvin-Benson, ocorre no estroma, nome dado à matriz líquida não clorofilada do cloroplasto, e foi estudada pelos bioquímicos norte-americanos Melvin Calvin (1911- 1997), Andrew Benson (1917-2015) e James A. Bassham (1922-2012) no final da década de 1940.

Ciclo Calvin YouTube
The Calvin cycle, Calvin-Benson-Bassham (CBB) cycle, reductive pentose phosphate cycle (RPP cycle) or C3 cycle is a series of biochemical redox reactions that take place in the stroma of chloroplast in photosynthetic organisms.
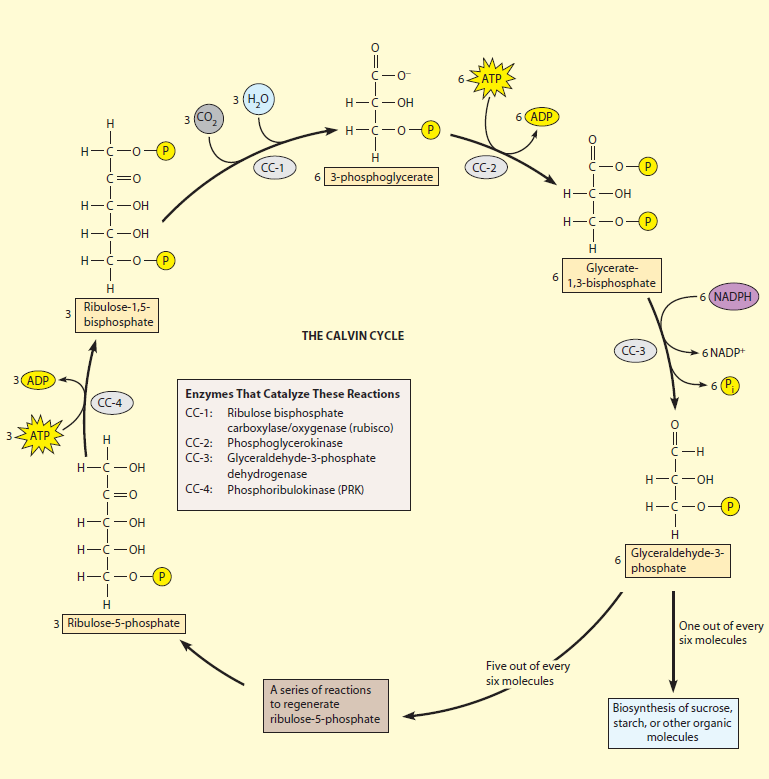
The Calvin Benson cycle
Calvin-Benson-Bassham Cycle. Page ID. Photosynthesis is responsible for creating NADPH and ATP and the Calvin-Benson-Bassham cycle (CBB) uses those high energy molecules to drive the production of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G-3-P). G-3-P can then be used to synthesize hexose sugars which are the primary source of nutrients for heterotrophs.